Discover the Power of Phonics – A Proven Method for Teaching Reading by Mastering Phonemes and Graphemes.
International Phonics Alphabet (IPA)
Understanding the IPA – International Phonetic Alphabet:
The IPA is a system of symbols representing word pronunciations. Every dictionary employs it, but many are unfamiliar with its usage.
For example, the word “dictionary” appears with funny symbols beside it. These symbols are the IPA, each representing a “phoneme,” a sound unit with meaning.


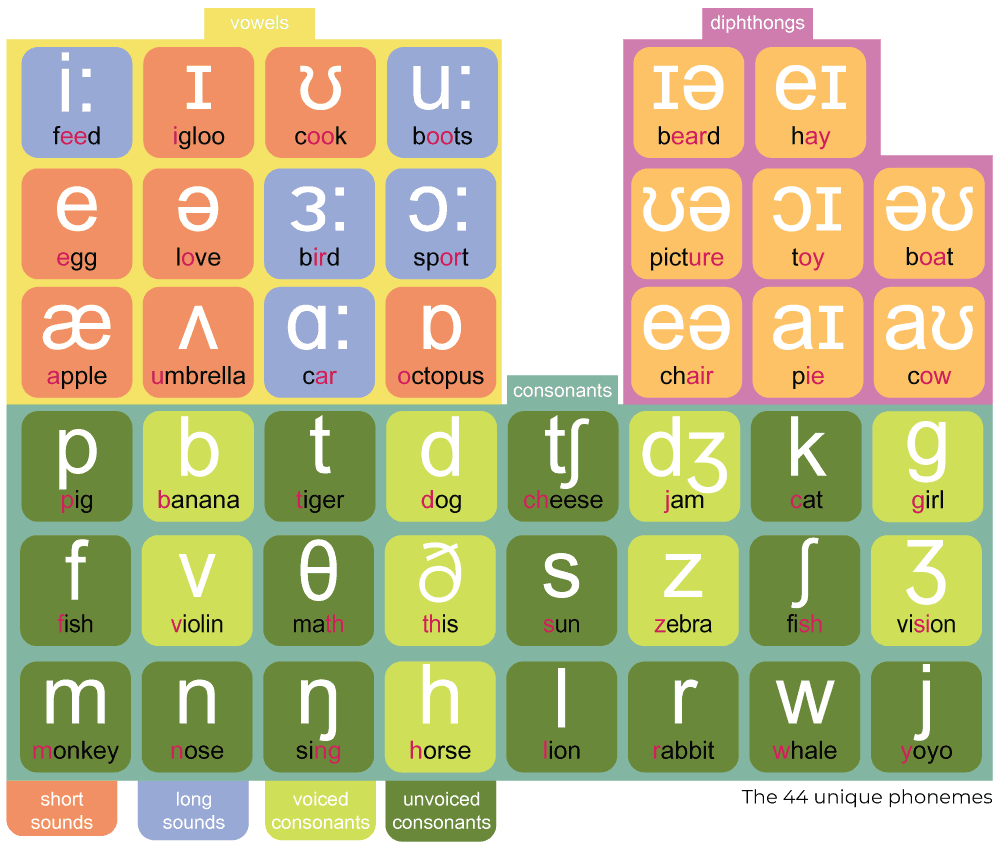
English contains 44 phonemes, categorized into vowels, consonants, and diphthongs.
Vowels consist of 12 phonemes – 5 long and 7 short sounds.
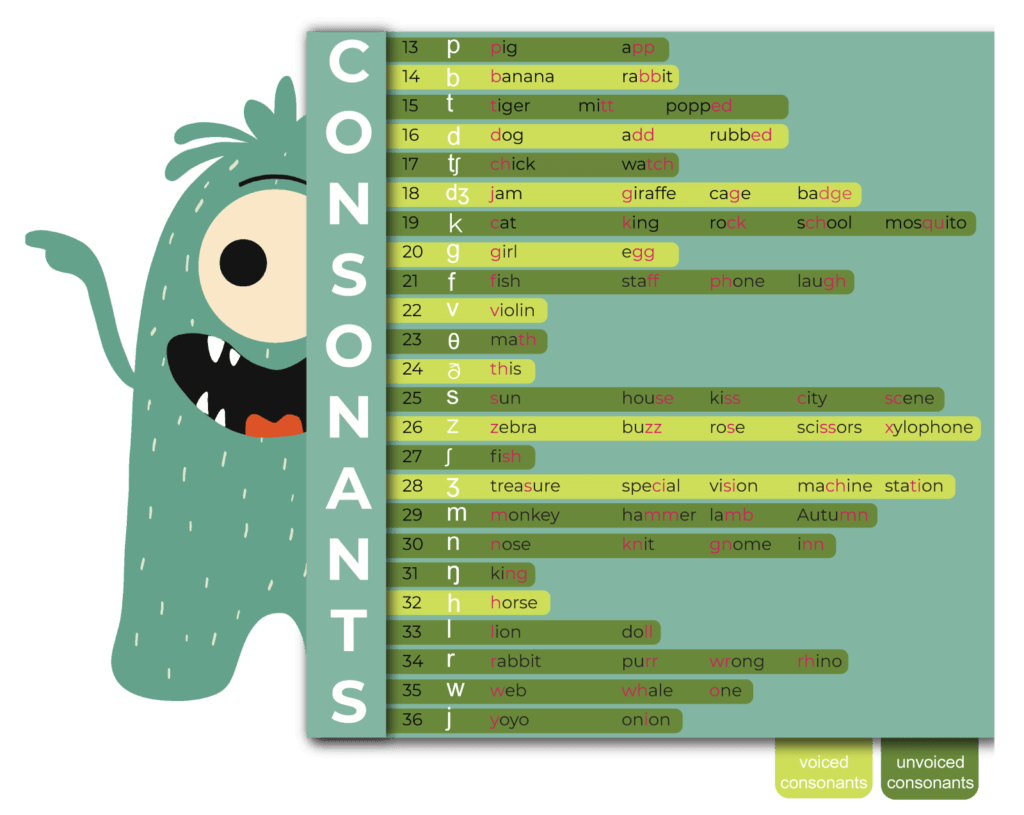
Consonants encompass 24 phonemes – 15 voiced and 9 unvoiced.
Lastly, there are 8 phonemes in the diphthong group.
Explore the IPA Phonemic Chart with all 44 sounds represented below.
* Sounds can vary with different regional accents
IPA Phonemic Chart
Unraveling Phonemes and Graphemes:
Sometimes, letter combinations create phonemes, and a single letter can represent multiple phonemes!
Feeling a bit puzzled? No need to fret!
Explore Phonemes – Sounds and Their Corresponding Graphemes (Written Letters from the Alphabet).
Let’s break it down for you!
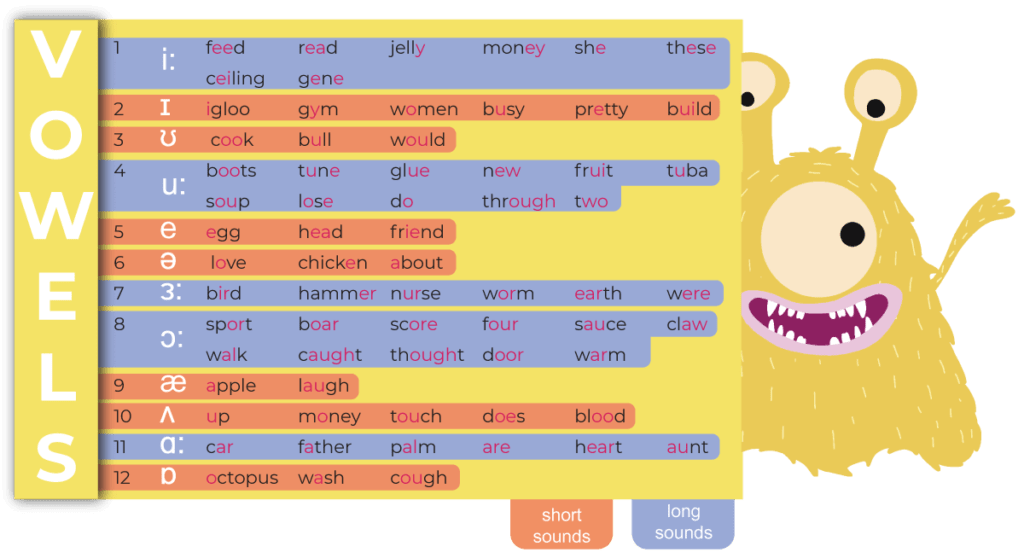
Vowels
Discover the 12 Vowels with Various Grapheme Representations:
Consonants
Explore the 24 Consonants with Diverse Grapheme Representations:
Diphthongs
Discover the 12 Diphthongs with Diverse Grapheme Representations:

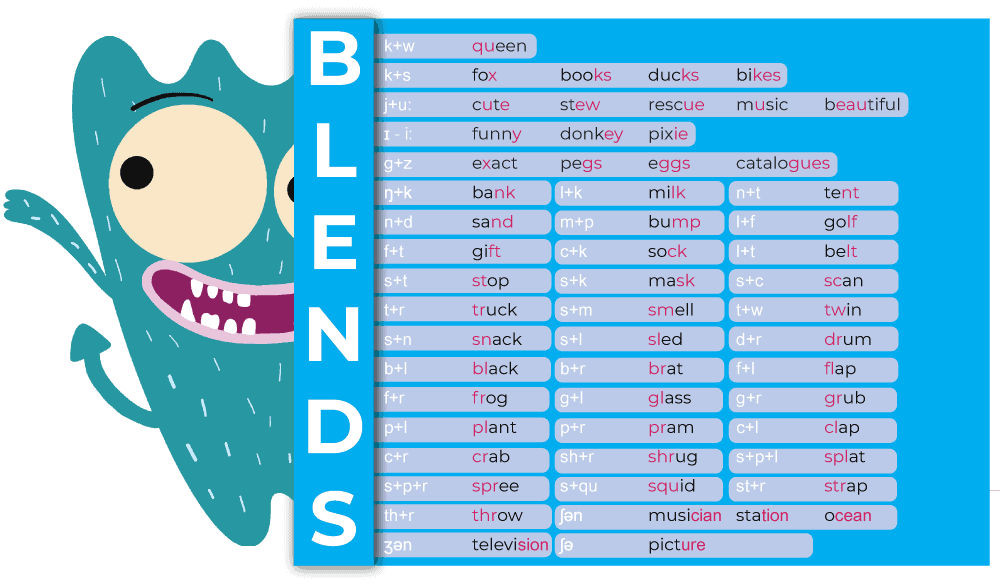
Blends
Blends are Formed by Combining Two or Three Letters to Create Consonant Sounds.
Phonics Glossary
Blending – This involves looking at a written word, looking at each grapheme, and using knowledge of GPCs to work out which phoneme each grapheme represents and then merging these phonemes together to make a word. This is the basis of reading.
Digraph – A grapheme containing two letters that makes just one sound (phoneme).
Grapheme – A way of writing down a phoneme. Graphemes can be made up of 1 letter e.g. p, 2 letters e.g. sh, 3 letters e.g. tch, or 4 letters e.g. eigh.
GPC – This is short for Grapheme Phoneme Correspondence. Knowing a GPC means being able to match a phoneme to a grapheme and vice versa.
IPA – The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) is an alphabetic system to provide a unique symbol for each distinctive sound in a language – that is, every sound, or phoneme, that serves to distinguish one word from another.
Phoneme – The smallest unit of sound. There are approximately 44 phonemes in English (it depends on different accents). Phonemes can be put together to make words.
Trigraph – A grapheme containing three letters that makes just one sound (phoneme).
Segmenting – This involves looking at a written word, looking at each grapheme, and using knowledge of GPCs to work out which phoneme each grapheme represents and then merging these phonemes together to make a word. This is the basis of reading.